Elevated Police Turnover Following the Summer of George Floyd Protests: A Synthetic Control Study
Abstract
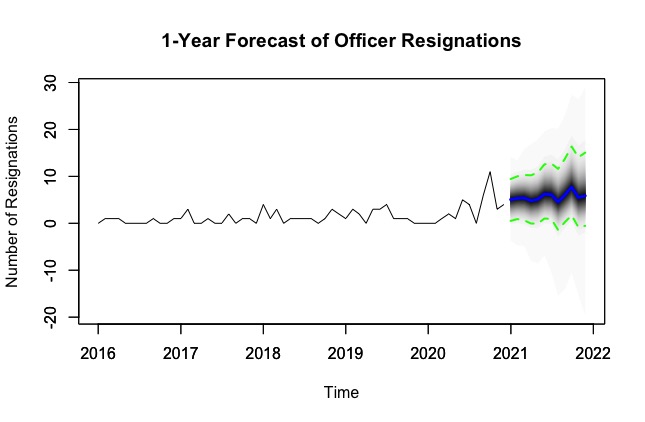
Several of the largest U.S. police departments reported a sharp increase in officer resignations following massive public protests directed at policing in the summer of 2020. Yet, to date, no study has rigorously assessed the impact of the George Floyd protests on police resignations. We fill this void using 60 months of employment data from a large police department in the western United States. Bayesian structural time series modeling shows that voluntary resignations increased by 279% relative to the synthetic control, and the model predicts that resignations will continue at an elevated level. However, retirements and involuntary separations were not significantly affected during the study period. A retention crisis may diminish police departments' operational capacity to carry out their expected responsibilities. Criminal justice stakeholders must be prepared to confront workforce decline and increased voluntary turnover. Proactive efforts to improve organizational justice for sworn personnel can moderate officer perceptions of public hostility.